This is the public consultation page for the proposed methodology and process for biodiversity crediting in boreal forests.
Research
Proposed methodology and process for biodiversity crediting in boreal forests is a part of research project on “Mechanisms and opportunities for financing of forest biodiversity” at Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences SLU.

The research team
The research on “Mechanisms and opportunities for financing of forest biodiversity” is conducted by Aleksandra Holmlund and is part of litentiate studies.Martin Pilstjärna (PhD) has actively contributed with input and design of biodiversity methodologies.The research is supervised by Prof. Dr. Tomas Lundmark.
TEAM
Webinar recording and a link to the recording
The recording wa disturbed around 5th to 8th minute by some external noise.We apologies for the incovenience.
Biodiversity crediting process description
PARTNERS
Why biodiversity credits?
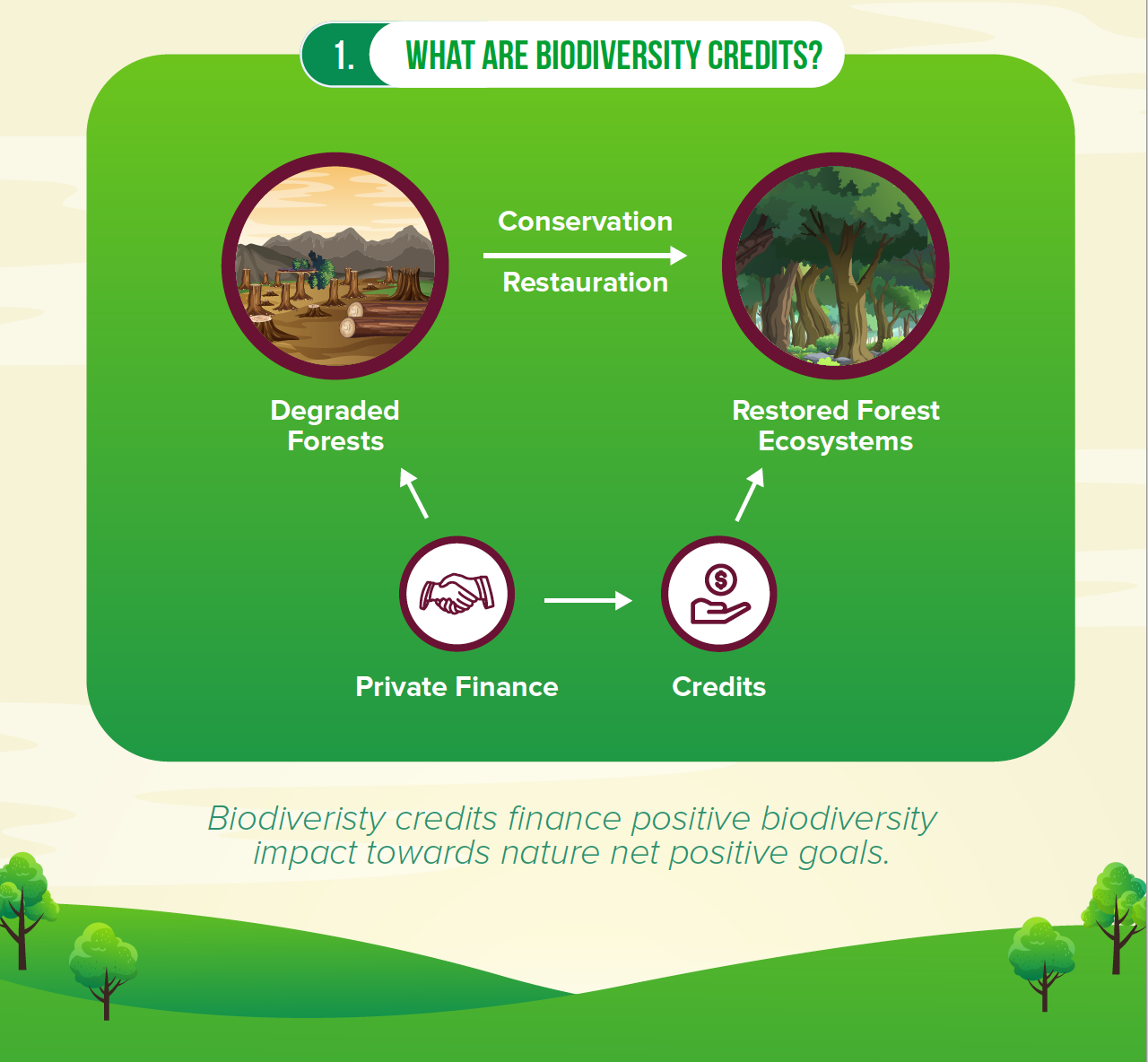
There is a strong economic justification for incentives that encourage private land owners towards nature focused management of their land including payments for ecosystem services as well as confirmation of benefits of ecological restoration. The rationale behind market driven instruments for biodiversity conservation is that positive and negative impacts on biodiversity can be measured and represented as credits and debts, and as such can be integrated in economic-decision making. A business may have to pay for regulatory mitigation of its biodiversity impact, or may wish to contribute to a voluntary net-positive impact on ecosystems thus improving its image and reputation towards its customers. Likewise, if a landowner may gain a profit from protecting or restoring a habitat, they may provide more habitat protection than they would have done without compensation.


Biodiversity credit vs offsets
Biodiversity offsets are relatively common in many countries and are used to compensate for biodiversity loss with a goal to create a no net loss, or even a net gain of biodiversity often connected to land exploitation for building, mining and other activities with negative environmental impact. Biodiversity offsets are often a legal requirement in m any countries in order to obtain, for example, an exploitation permit by a state agency.Biodiversity credits, on the other hand, are not a legal requirement, and can therefore be used to describe a positive biodiversity impact resulting from a targeted action towards that purpose.
What is a biodiversity credit?
Biodiversity credits are a mechanism that allows individuals and companies to invest in environmental projects that contribute to a richer biodiversity. A credit itself is a legal document, analog or digital, describing where the environmental action has taken place, who has developed it, according to what methodologies, and that it has been certified according to a certain system. Biodiversity credits may be transacted after issuance.
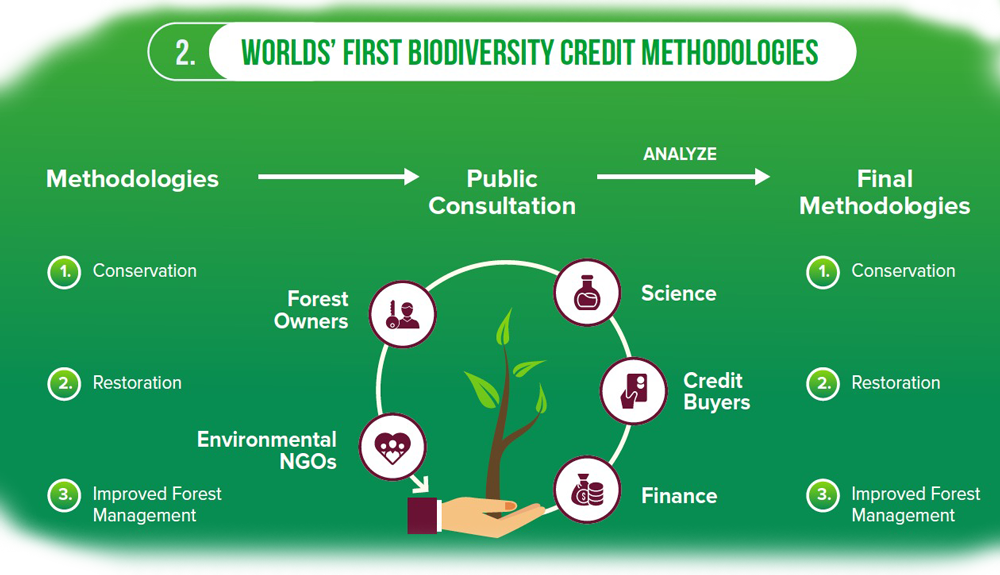
The public consultation process
We are asking the interested stakeholders to comment and give us their opinion on the proposed methodologies and crediting process.
Public consultation process successfully completed
The public consultation process has been successfully completed, with a range of
stakeholders leaving their comments on the proposed methodologies. We thank everyone
who participated in the public consultation for their time and effort.
We are working on synthesizing the comments and will be posting them here as soon as
possible.
Object of public consultation
- Methodology for improved biodiversity in boreal forests through restauration,
- Methodology for improved biodiversity in boreal forests through improved forest management of working forests, and
- Methodology for improved biodiversity in boreal forests through conservation.
We have also developed a biodiversity assessment method and a biodiversity valuation and calculation method that should be used for developing biodiversity credit projects.
Please find the documents for public consultation here:
Questions for public consultation
Are you a forest owner? Please give us your opinion on:
- Would you be interested in testing a biodiversity credit project?
- Is there something in the proposed methods that you don’t think will work in practice?
- Do you have any concerns about the proposed methods?
Are you a potential buyer of biodiversity credits? Please give us your opinion on:
- Would you be interested to buy biodiversity credits created according the proposed methods?
- Is biodiversity net increase something you can and would like to incorporate in your ESG reporting?
- What granularity of the biodiversity metrics does your organization need for the reporting purposes?
Are you an NGO representative or a scientist?
Please comment on whole or for you relevant parts of methodologies and processes.
Please use the contact form to share your comments and views.
Public consultation schedule
Planned information webinars:
May 25, 7-8 pm CET
June 3, 9-10 am CET
If you want to receive a webinar link, please make a request through the contact form.
Webinar recording and a link to the recording
The recording wa disturbed around 5th to 8th minute by some external noise.We apologies for the incovenience.
A pilot project will be carried out during September 2022 to test and improve biodiversity
credit methodologies and to carry out a test transaction. We will regularly post updates
about progress here.




